Data Matrix Code vs QR Code? [Comparative Analysis]
In this digitally driven day and age, barcoding technology forms the backbone of numerous routine operations in various sectors. While there are several types of barcodes, the spotlight in this piece will be on two in particular - Data Matrix Code and QR Code.

Understanding Data Matrix Code
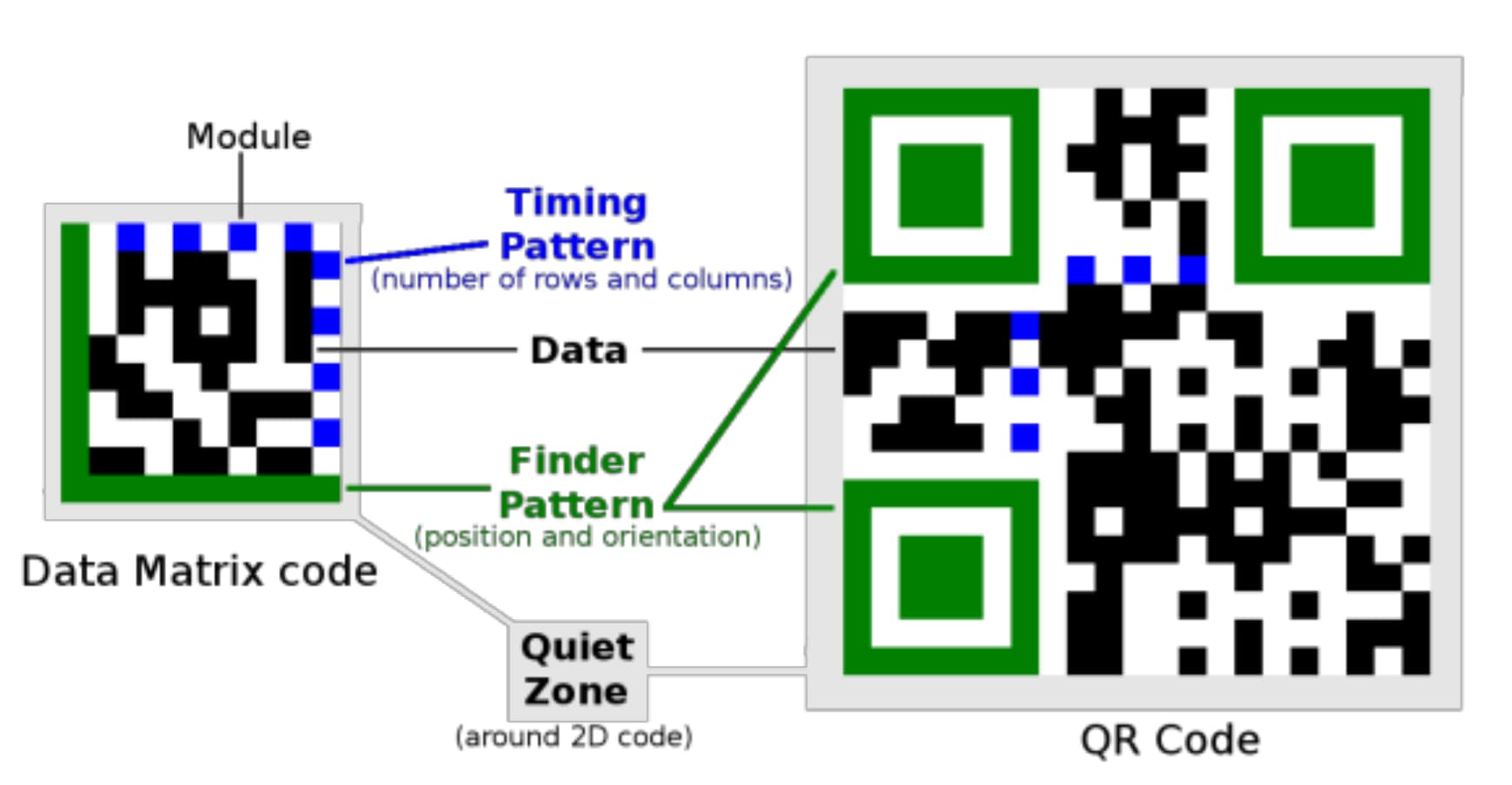
- Data Matrix Code (DMC) is a type of 2D barcode with black and white square modules.
- Widely adopted in industries like electronics, automotive, and aerospace.
- Capable of storing large volumes of data, including text and numeric data up to 1556 bytes or 2,335 alphanumeric characters.
- Requires a special scanner to decode.

DMC is frequently used in the electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries due to its high tolerance for harsh conditions and its capacity to hold large data volumes, including text and numeric data up to 1556 bytes, or 2,335 alphanumeric characters. Despite these significant strengths, DMC also has limitations such as less familiarity among the general public and the requirement of a special scanner to decode.
Understanding QR Code
- Quick Response (QR) Code is a square-shaped 2D barcode with distinctive smaller squares at three corners.
- Popular in marketing and retail sectors due to easy smartphone scanning.
- Can hold numeric data up to approximately 7,089 characters and 4,296 alphanumeric characters.
- Larger in physical size compared to DMC at similar data levels.
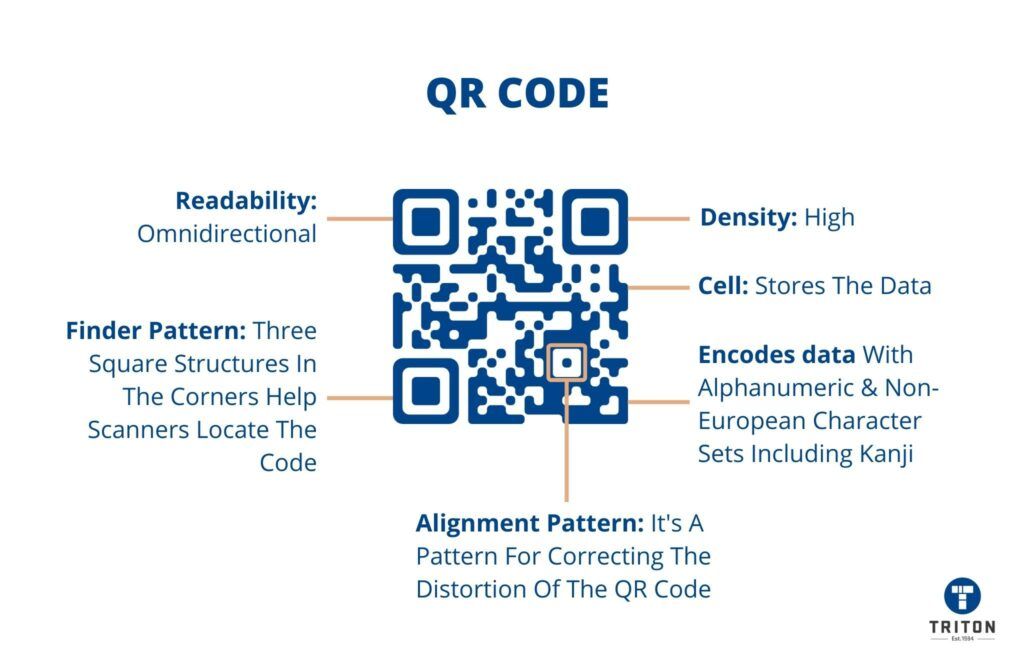
Quick Response (QR) Code is another 2D barcode but is recognizably unique with its square shape and distinctive smaller squares at three of its corners. This globally recognized barcode has gained immense popularity, especially in the marketing and retail sectors. The ability to be easily scanned by smartphones is one of the reasons behind its wide adoption.
A QR Code can accommodate numeric data up to approximately 7,089 characters and 4,296 alphanumeric characters. It is mostly used on websites, business cards, and advertisements, offering a quick and easy way to direct users to a website or app. However, while being user-friendly and versatile, QR Codes are more vulnerable to damage and are also significantly larger in physical size compared to DMC at similar data levels.
| Aspect | Data Matrix Code | QR Code |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Black and white square modules arranged in a square or rectangular pattern | Square-shaped with smaller squares at three corners |
| Industries | Electronics, automotive, aerospace | Marketing, retail |
| Data Capacity | Up to 1556 bytes or 2,335 alphanumeric characters | Up to 7,089 numeric characters or 4,296 alphanumeric characters |
| Scanner Requirement | Requires a special scanner | Can be easily scanned by smartphones |
| Robustness | High tolerance for harsh conditions | Vulnerable to damage, less durable |
| Error Correction | Can handle damage up to 20-25 percent | Can retain information even when partially damaged up to 30 percent |
| Functionality | Handles numeric and alphanumeric data | Can link directly to websites |
| Readability | Requires specific scanner | Easily scanned by smartphones |
| Real-world Usage | Preferred in manufacturing, aerospace, electronics | Prevalent in marketing, retail |
Comparative Analysis of Data Matrix Code vs QR Code
When comparing DMC and QR Code, several factors come into play:
- Capacity: DMC can hold a larger amount of data in a more compact space, an advantage when printing space is limited. QR Codes, on the other hand, while able to store a surprising amount of data, end up substantially larger for equivalent data levels.
- Size: As mentioned above, DMC's compactness is a considerable advantage, especially in industrial applications where space might be at a premium. QR Codes, meanwhile, tend to be more visible due to their larger size, making them more suitable for use in marketing and advertising.
- Error Correction: Both DMC and QR Codes have robust error correction capabilities. However, QR Codes offer a higher redundancy level, allowing them to retain information even when partially damaged up to 30 percent, whereas DMC can handle damage up to 20-25 percent.
- Functionality: Both the DMC and QR Code can handle numeric and alpha-numeric data, with the QR Code additionally capable of linking directly to websites, which has greatly contributed to its ubiquitous use in the commercial sector.
- Readability: QR Codes are easily scanned by any smartphone, making them highly accessible to the general public. Contrastingly, to read a DMC, you need a specific scanner, making them more suited to professional or industrial uses where such equipment is commonly available.
- Real-world usage: Given its robustness and compactness, DMC is preferred in environments such as manufacturing where durability and space-efficiency are key. Conversely, QR Codes are more prevalent in commercial and customer-facing applications due to their easy scanability with common devices such as smartphones.
Given these differences, your choice between Data Matrix Code and QR Code will invariably depend on the specific requirements of your application. It is essential to consider both the data you want to encode and the scanning abilities of the end-user when deciding which to opt for.
In conclusion, both Data Matrix Codes and QR Codes offer unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these key differences can help you make an informed decision, ensuring you choose the right barcode for your specific needs.
Making the decision to use either a Data Matrix Code or QR Code may seem overwhelming at first, but the decision really boils down to the specifics of your individual application needs. Let's delve into this in more detail.
GS1 DataMatrix |
| QR Code | Data Matrix |
|
|
| |
Uses GS1 element string syntax | Uses GS1 Digital Link URI syntax | ||
Situational Analysis – Suggest scenarios when to use one over the other
To illustrate better when to consider using a Data Matrix Code or QR Code, let's look at some real-world examples:
- Inventory Control: If you are tracking components in an industrial setting where space is at a premium and durability is crucial, a Data Matrix Code with its high data capacity and robustness proves to be the superior choice.
- Marketing Campaigns: For instances where you need to link a physical element to an online platform, QR Codes are the go-to option due to their ability to be scanned easily using a smartphone's camera and directing users straight to a web link.
- Product Labeling in Retail: In a retail setting where the ease of scanning using consumer devices is essential, QR Codes, again, are a better option.
- Aerospace and Defense: These sectors often require the ability to encode vast amounts of data into tiny items, where durability under harsh conditions is a must - conditions ripe for the use of Data Matrix Code.
Consideration of reader hardware and software
Discuss how the choice of code can be influenced by the devices or technology available to read them
Hardware and software also significantly influence the decision to use either a Data Matrix Code or QR Code.
- General Public Accessibility: For applications intending for wide public engagement, QR Codes are the better choice. Most modern smartphones with a camera and barcode scanning app can easily read QR Codes. This quality makes QR Codes ideal for quick information sharing, links to websites, or marketing campaigns.
- Industrial Applications: Data Matrix Codes are usually decoded using industrial readers. These readers come with specific software that allows for high-speed decoding and increased read rates, even under harsh conditions and at varying distances. Such systems are commonly found in manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics markets.
- DMC excels in large data capacity and robustness for industrial settings.
- QR Codes are prevalent in consumer-facing roles for their ease of use and link to online platforms.
- Choose based on specific needs, considering data type, printing space, scanning equipment, and end-user capabilities.
In summary, choosing between a Data Matrix Code and a QR Code depends on key factors tailored to your specific needs. QR Codes excel in easy scanning and consumer engagement, while Data Matrix Codes shine in handling large data, durability, and space efficiency, particularly in industrial environments. Assessing your application requirements and end-users' capabilities is crucial for making the right choice.
In conclusion, both Data Matrix Codes and QR Codes offer unique benefits. Data Matrix Codes are ideal for industrial applications with limited printing space and high durability needs, whereas QR Codes are more suitable for consumer-facing roles like marketing and retail, thanks to their easy smartphone scanning and website linking capabilities.
Ultimately, the decision boils down to your specific situation and requirements. Factors such as data type, printing space, scanning equipment availability, and end-user capabilities should be thoroughly evaluated to ensure effective utilization of barcode technology for smooth data management processes.




