What is QR Code: Uses, Functions, History and Security Measures
A QR code is a two-dimensional barcode that stores data in black and white square patterns, readable by any smartphone camera. Unlike traditional barcodes limited to 20 characters, a single QR code holds up to 7,089 numeric characters. With 2.2 billion monthly scanners worldwide in 2026, QR codes bridge physical objects and digital information.
How Do QR Codes Work?
QR code is a two-dimensional matrix barcode that encodes data in a grid of black and white modules, scannable from any angle by a smartphone camera. It stores up to 7,089 numeric or 4,296 alphanumeric characters and uses built-in error correction to remain readable even when partially damaged.
QR codes encode information into a grid of black and white modules arranged on a square background. When you point your phone camera at one, the scanning software reads the pattern in three stages.
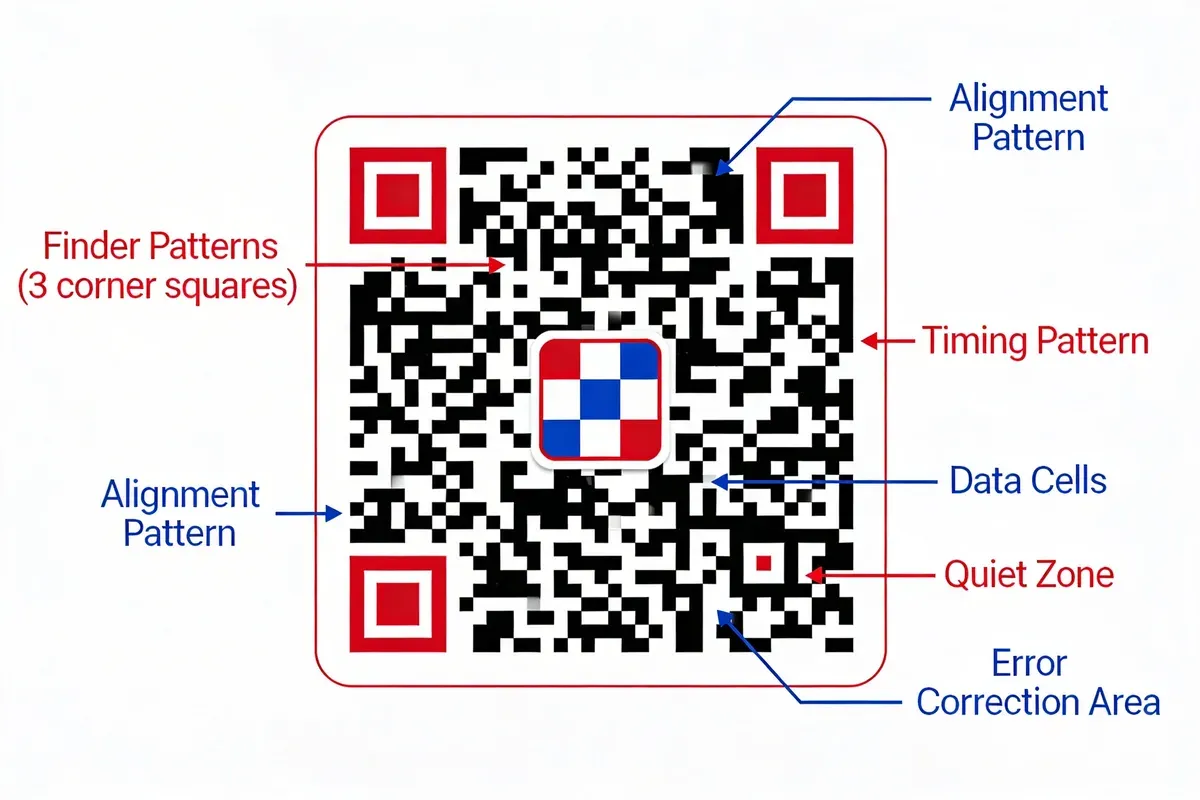
- Detection and orientation: Three large square "finder patterns" sit in three corners of every QR code. Your camera locates these first, which tells the scanner where the code is and what angle it's at. A fourth, smaller alignment pattern in the remaining corner corrects for perspective distortion if you're scanning at an angle.
- Grid reading: Timing patterns (alternating black-white strips connecting the finders) establish the module grid. The scanner reads each module as a binary 1 (black) or 0 (white), then assembles the full binary string from the data cells filling the interior.
- Error correction and decoding: Reed-Solomon error correction reconstructs missing or damaged data. Depending on the correction level (L, M, Q, or H), a QR code can lose 7% to 30% of its modules and still scan correctly. The binary string is then decoded into its original format: a URL, plain text, contact card, or Wi-Fi credentials.
This entire process takes under 200 milliseconds on modern smartphones. Both iOS (built into the Camera app since iOS 11) and Android (native since Android 9) can scan QR codes without any third-party app.
Key Components of a QR Code
| Component | Function | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Finder patterns (3) | Locate and orient the code | Enable scanning from any angle or distance |
| Alignment pattern | Compensate for perspective distortion | Allows scanning even when tilted |
| Timing patterns | Define the module grid spacing | Accurate row/column count for decoding |
| Quiet zone | Blank border around the code | Prevents background interference with scanning |
| Data cells | Store the encoded information | The actual payload: URLs, text, or binary data |
| Error correction | Rebuild damaged or obscured data | Codes stay readable at up to 30% damage |
History of QR Codes
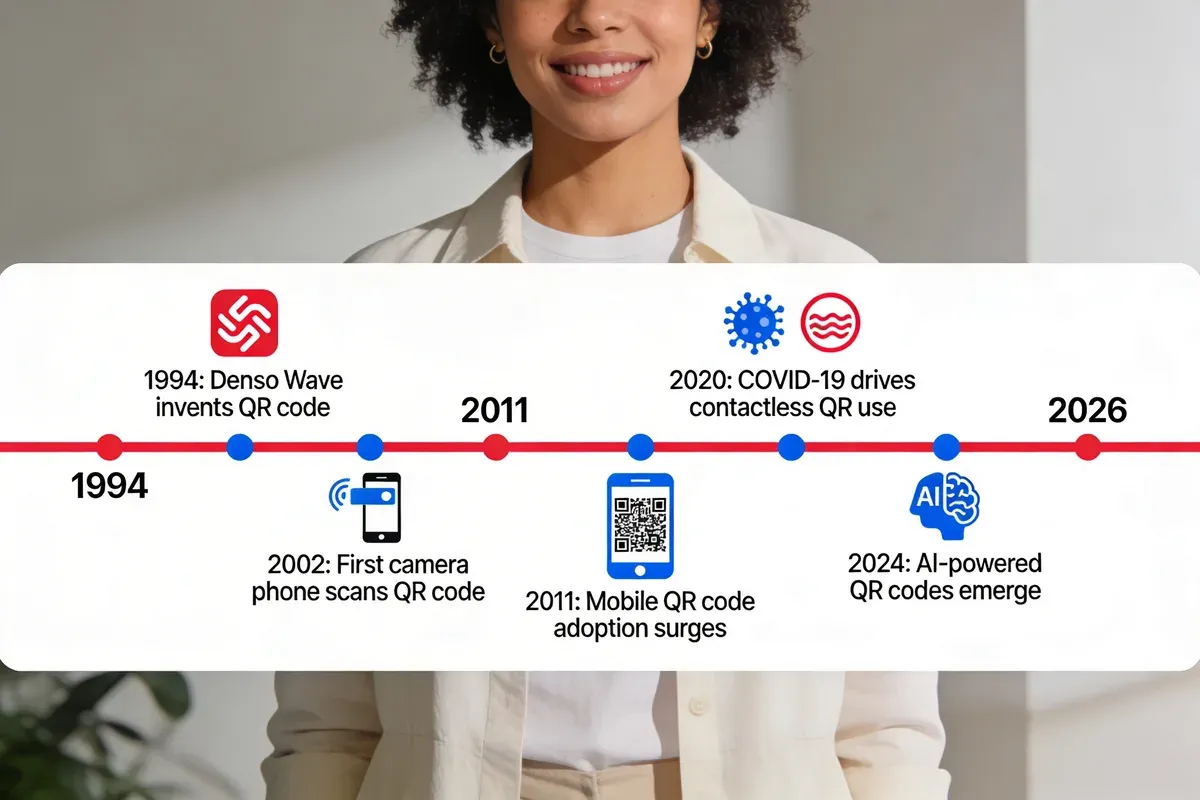
The QR code was born from a manufacturing bottleneck. In 1994, Masahiro Hara's team at Denso Wave needed to track vehicle components faster than the one-dimensional barcodes Toyota's production lines relied on. Traditional barcodes stored just 20 characters. Hara's solution packed up to 7,089 numeric characters into a two-dimensional grid that scanners could read ten times faster.
Denso Wave made a decision that changed the technology's trajectory: they released the QR code specification publicly, waiving patent enforcement. This open approach let anyone create and use QR codes without licensing fees.
Key milestones in QR code history:
- 1994: Denso Wave invents the QR code for Toyota's assembly line tracking
- 2000: ISO standardisation (ISO/IEC 18004) formalises the specification globally
- 2002: Sharp releases the first camera phone with a built-in QR reader in Japan, triggering consumer adoption
- 2011: Smartphone penetration crosses 35% in the UK and US, but scanning still requires third-party apps
- 2017-2018: Apple (iOS 11) and Google (Android 9) add native QR scanning to their camera apps, removing the adoption barrier
- 2020-2021: COVID-19 drives contactless QR adoption for menus, check-ins, vaccine passports, and payments
- 2024-2026: AI-generated custom QR codes, dynamic analytics, and QR payment market growth push the technology into a new phase
What is the Difference Between a QR Code and a Barcode?
The core difference is dimensional. A traditional barcode stores data in one direction (horizontal lines), while a QR code stores data in two directions (a grid of squares). This means QR codes hold roughly 350 times more information in the same physical space.

| Feature | Traditional Barcode (1D) | QR Code (2D) |
|---|---|---|
| Data capacity | Up to 20 alphanumeric characters | Up to 7,089 numeric or 4,296 alphanumeric |
| Data direction | Horizontal only | Horizontal and vertical (matrix) |
| Scanning angle | Must align with the bars | Any angle, 360 degrees |
| Error correction | None | Up to 30% damage tolerance |
| Data types | Numbers and basic text | URLs, text, contacts, Wi-Fi, GPS, files |
| Customisation | Limited (line thickness) | Colours, logos, shapes, frames |
| Scanner required | Dedicated laser scanner | Any smartphone camera |
| Common use | Retail product identification (UPC/EAN) | Marketing, payments, authentication, menus |
For product identification in retail and warehousing, traditional barcodes remain the standard because they're cheaper to print and existing infrastructure supports them. QR codes are the better choice when you need to encode more data, want customers to scan with their phones, or need error correction for outdoor or high-wear environments. For a deeper comparison, see our QR code vs barcode guide.
Types of QR Codes
QR codes come in several variants designed for different storage needs, physical sizes, and security requirements. The two categories most people encounter are static and dynamic, but the full family includes seven distinct types.

Static QR Code
Static QR codes encode data permanently at creation. The information (a URL, phone number, or text) is baked directly into the module pattern and can't be changed afterwards. They work offline, never expire, and don't require a hosting service. Best for: business cards, product labels, and any content that won't change.
Dynamic QR Code
A dynamic QR code contains a short redirect URL instead of the final destination. This means you can update where the code points without reprinting it. Dynamic codes also track scan data: number of scans, location, device type, and time. At QRCode.co.uk, we've found that marketing teams overwhelmingly prefer dynamic codes because they can A/B test landing pages and monitor campaign performance in real time.
Model 1 and Model 2
Model 1 is the original 1994 specification, limited to 14 x 14 modules. Model 2 improved on it with alignment patterns for better scanning at angles and larger storage capacity. Every modern QR code you encounter is Model 2. Model 1 is effectively obsolete.
Micro QR Code
Micro QR uses a single finder pattern instead of three, making it roughly 50% smaller than a standard QR code. It stores up to 35 numeric characters. Useful for electronic component labels, pharmaceutical packaging, and anywhere physical space is severely limited.
iQR Code
Developed by Denso Wave, iQR codes break the square constraint. They can be rectangular, which suits applications like narrow product labels or printed circuit boards where a square code won't fit. iQR also supports higher data density than standard QR.
Secure QR Code (SQRC)
SQRCs encrypt their data payload, requiring a specific decryption key to read the contents. The code looks identical to a regular QR code when scanned by a standard reader (it simply won't decode), but authorised scanners unlock the encrypted data. Used for confidential documents, access control, and anti-counterfeiting in pharmaceuticals.
Frame QR
Frame QR codes include a customisable canvas area in the centre of the code for logos, icons, or calls to action like "Scan Me." They maintain scannability while giving brands visual identity within the code itself. Popular in marketing campaigns where brand recognition matters.
| Type | Best For | Key Characteristic | Editable After Creation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static | Permanent labels, business cards | Data fixed at creation | No |
| Dynamic | Marketing campaigns, menus | Redirect URL, scan analytics | Yes |
| Model 2 | General purpose (standard) | Alignment patterns, high capacity | No |
| Micro QR | Small components, labels | Single finder, 50% smaller | No |
| iQR | Narrow labels, PCBs | Rectangular shape option | No |
| SQRC | Security, anti-counterfeiting | Encrypted data payload | No |
| Frame QR | Branded marketing | Central logo/canvas area | Depends on base type |
Why QR Codes Matter for Businesses in 2026
QR codes have moved from a novelty to a core marketing and operations channel. The numbers tell the story: according to Supercode, more than 2.2 billion people scan QR codes every month, reaching nearly 29% of all smartphone users globally.
- Near-universal marketer adoption: Bitly reports that 94% of marketers increased their QR code usage in the past year, making it one of the most widely adopted physical-to-digital tools in marketing
- Measurable offline-to-online bridge: Dynamic QR codes track scans by location, time, device, and campaign, giving marketers attribution data for print materials, packaging, and signage that was previously unmeasurable
- Payment infrastructure growth: According to Juniper Research, retail QR code payments will grow from 454 billion in 2025 to 741 billion in 2030, a 79% increase
- Low implementation cost: Static QR codes are free to generate and print. Dynamic codes from platforms like QRCode.co.uk offer analytics and editing without significant upfront investment
- Accessibility: No app download required. Every modern smartphone scans QR codes natively through the camera
According to QRCodeChimp, global QR code usage grew by 22% through 2025, and that trajectory is accelerating.
Common Uses of QR Codes in 2026
QR codes appear in nearly every sector where physical objects need to connect to digital experiences. Here are the applications driving the most adoption right now.

Marketing and Advertising
Brands place QR codes on print ads, billboards, product packaging, and direct mail to drive traffic to landing pages, app downloads, and promotional offers. Dynamic codes let marketing teams swap destinations mid-campaign without reprinting. One notable early example: GM placed QR codes on Chevrolet vehicles at SXSW Interactive, and according to Holtz Communications, while only 2% of attendees scanned the codes, the resulting media coverage generated 1.68 million impressions.
Payments and Retail
QR code payments are standard across Asia (Alipay, WeChat Pay) and growing fast in Europe and the Americas. Customers scan a merchant's QR code or display their own to complete a transaction without touching a terminal. This contactless flow, accelerated by the pandemic, continues to expand. Juniper Research projects the sector will nearly double by 2030.
Restaurants and Hospitality
Digital menus via QR codes replaced paper menus at most restaurants during COVID-19, and the change stuck. Guests scan a table-top code to view the menu, order, and pay from their phone. Hotels use QR codes for check-in, room service, Wi-Fi access, and local area guides. See the latest data in our hospitality QR code statistics report.
Events and Ticketing
QR code tickets eliminate paper waste and speed up entry. Event organisers issue unique QR codes per attendee that scanners verify in under a second. The codes can also store seating assignments, dietary preferences, and networking profiles. Our guide on QR codes in event management covers adoption data across the industry.
Product Authentication and Supply Chain
Luxury brands, pharmaceutical companies, and food producers assign unique QR codes to individual products. Consumers scan to verify authenticity and view supply chain history. Regulators use the same codes for traceability audits. The GS1 Digital Link standard formalises this approach, embedding product data directly in QR codes that replace traditional UPC barcodes.
Contactless Information Sharing
Business cards, Wi-Fi networks, map locations, and contact details can all be encoded in a QR code. Scanning a vCard QR code saves a contact directly to your phone. Scanning a Wi-Fi QR code connects you to the network without typing a password. Our QR code business card guide walks through the setup process.
According to a Digimarc study, nearly half of respondents had interacted with a QR code in the past three months, confirming that scanning behaviour is now habitual rather than occasional.
How to Create a QR Code
Creating a QR code takes under two minutes with a dedicated generator. Here's the process we recommend based on three years of building and testing QR code tools at QRCode.co.uk.
- Pick your content type: Decide what the code will encode: a URL, plain text, vCard contact, Wi-Fi credentials, PDF, or app store link. Each type has a specific input format, so choose before you start
- Enter your data: Paste the destination URL or fill in the relevant fields. For dynamic codes, the generator creates a short redirect URL that points to your destination, so the QR pattern stays compact regardless of how long the target URL is
- Choose static or dynamic: Static codes are permanent and free. Dynamic codes cost a small monthly fee but let you edit the destination, track scans, and retarget. For any marketing use, go dynamic
- Customise the design: Add your brand colours, a centre logo, and a frame with a call to action. Keep customisation moderate. High error correction (level H, 30%) compensates for logos covering data modules, but excessive decoration can block scanning
- Test before printing: Scan the code with at least two devices (one iOS, one Android) at arm's length and in low light. If it doesn't scan instantly, reduce the logo size or increase the code resolution
- Download in the right format: Use SVG or PDF for print (scalable without pixelation). Use PNG for digital. Never scale a raster QR code image below its original resolution
- Print at the right size: Minimum 2 cm x 2 cm for close-range scanning (business cards, product labels). For billboards or signage, use 10:1 scan-distance-to-size ratio. A code viewed from 3 metres should be at least 30 cm wide
Are QR Codes Secure?
QR codes themselves don't carry viruses or malware. They're data containers, exactly like a URL typed into a browser. The security risk comes from where the code sends you, not from the code itself.
Common QR Code Threats
- QR phishing (quishing): Attackers create QR codes linking to fake login pages that mimic banks, payment processors, or corporate portals. The victim scans, sees a convincing page, and enters credentials
- Code replacement: Physical QR codes in public spaces (parking meters, restaurant tables, event posters) get covered with a sticker bearing a malicious code. The visual similarity between any two QR codes makes this hard to spot
- Forced downloads: A QR code can trigger an automatic file download. If the file contains malware and the user opens it, their device is compromised
Thomas Wilson, Senior Analyst at Juniper Research, warns: "In unattended and open environments, QR code payments are highly vulnerable to phishing attacks. It is essential that uniform QR payment standards featuring strict security controls are implemented across regions."
How to Scan QR Codes Safely
- Preview the URL before opening: Both iOS and Android show the destination URL in a notification banner. Check that the domain looks legitimate before tapping
- Check for physical tampering: If a QR code on a poster or sign looks like a sticker placed over another code, don't scan it
- Use your phone's built-in scanner: The native camera apps on iOS and Android include URL safety checks. Third-party scanner apps from Kaspersky and Avira add an extra layer of link verification
- Never enter credentials immediately after scanning: If a QR code takes you to a login page, navigate to the site manually through your browser instead
- Keep your OS updated: Security patches close vulnerabilities that malicious downloads might exploit
For businesses generating QR codes, use dynamic codes from a trusted platform. If a linked destination is compromised, you can update the redirect instantly without reprinting the physical code.
Common QR Code Mistakes to Avoid
- Printing too small: A QR code under 2 cm x 2 cm won't scan reliably from a normal distance. We've tested hundreds of print sizes at QRCode.co.uk, and codes below 1.5 cm fail on about 40% of older phone cameras. Always test at the intended viewing distance
- Skipping the quiet zone: The blank border around a QR code isn't decorative. It's part of the specification. Cropping it or placing the code against a busy background causes scanning failures
- Using static codes for campaigns: If you print 10,000 flyers with a static QR code and the landing page URL changes, those flyers are wasted. Dynamic codes solve this entirely
- Over-customising the design: Adding a large logo, reducing contrast, or using colours with insufficient difference between the dark and light modules can make codes unscannable. Always test custom designs on multiple devices before a print run
- No call to action: A bare QR code without context ("Scan for the menu", "Scan to pay", "Scan for 20% off") reduces engagement. People need a reason to pull out their phone
Frequently Asked Questions About QR Codes
How does a QR code work?
A QR code stores data in a grid of black and white squares. Your smartphone camera detects the code using three corner finder patterns, reads the grid as binary data, applies error correction to fix any damaged modules, and decodes the result into usable information like a URL, text, or contact card. The process takes under 200 milliseconds.
What is a QR code used for?
QR codes are used for payments, marketing campaigns, restaurant menus, event tickets, product authentication, Wi-Fi sharing, business cards, and supply chain tracking. Any situation where you need to connect a physical object to digital content is a potential QR code application. According to ScanQueue, 89 million Americans scanned a QR code in 2025, with that number projected to exceed 100 million in 2026.
Are QR codes free to create?
Yes. Static QR codes are free to generate on platforms like QRCode.co.uk and don't expire. Dynamic QR codes, which offer editing and scan tracking, typically require a paid subscription. Basic dynamic codes start at a few pounds per month.
Can QR codes expire?
Static QR codes never expire because the data is encoded directly in the pattern. Dynamic QR codes depend on a redirect service. If the service subscription lapses or the provider shuts down, the redirect stops working. The code itself remains scannable, but it leads nowhere. Learn more in our guide on how long QR codes last.
What is the difference between a static and dynamic QR code?
A static QR code permanently encodes your data (a URL, text, or contact). A dynamic QR code encodes a short redirect URL that you control. You can change the destination, track scan analytics, and set time-based rules without altering the printed code. Dynamic codes are better for marketing. Static codes are better for permanent information. Read our full dynamic QR code guide for a detailed breakdown.
What is the history of QR codes?
Masahiro Hara at Denso Wave invented the QR code in 1994 to track Toyota automotive parts. The technology went public in 2000 via ISO standardisation, reached consumers through camera phone integration in 2002 (Japan), became native to iOS and Android in 2017-2018, and saw massive global adoption during the 2020-2021 pandemic for contactless operations.
QR Codes in 2026 and Beyond
QR code technology isn't slowing down. Three trends are shaping where it goes next.
AI-generated custom designs. New tools use generative AI to create QR codes that blend into artistic designs, product photography, and brand imagery while remaining fully scannable. This pushes QR codes from a utility into a design element.
Standardised digital product passports. The EU's Digital Product Passport regulation will require QR codes on products sold in Europe, linking to sustainability, recyclability, and supply chain data. GS1's Digital Link standard is the leading framework for this.
Deeper analytics integration. Dynamic QR code platforms now connect scan data to CRM systems, Google Analytics, and Meta Pixel, giving marketers the same attribution granularity for physical touchpoints that they've had for digital ads. The adoption across industries continues to accelerate as these integrations mature.
Whether you're running a small business in the UK, managing marketing campaigns, or organising events, QR codes are a practical, low-cost channel worth building into your workflow. Start with a free static code to test the concept, then move to dynamic codes when you need tracking and flexibility.

